THE GREAT NATION OF ISLAM
The 6th century Arabs of Makkah in the Arabian Peninsula were the descendants of Ismail (Ishmael as named in the Old Testament), the first son of the Profit Ibrahim (Abraham).
Islam, the Promised Great Nation:
The nation of Islam, is the fulfillment of Gods promise to Ibrahim & to his wife Hagar as revealed in the Book of Genesis of the Old Testament.
In Genesis 17:20: God said to Abraham:
“And as for Ishmael, I have heard you: I will surely bless him; I will make him fruitful and will greatly increase his numbers. He will be the father of twelve rulers, and I will make him into a great nation.”
And as also revealed in Genesis chapter 21:18 when the Angels spoke on the name of God to Hagger (when she and her child were left in the desert suffering thirst and despair):
“Arise, lift up the lad, and hold him in thine hand; for I will make him a great nation.”
There are no further references in any of the books of the Old Testament and the Bibles, to the Great Nation which God promised it will come out of the descendants of Ishmael. By the time these holy books were revealed and written, the great nation has not yet appeared.
The continuation of the above biblical story was revealed in the Muslim’s holy book the “Quran”, and out of the descendants of Ismail; after more than twenty centuries, came the Prophet Mohammed Bin Abdullah (saas) to deliver the message of Islam.
The message of Islam without any doubt, established the greatest nation known to mankind during such a short period, within one hundred years, Islam covered most of the old world, from the shores on the Atlantic ocean till the edges of China. No army could cover such enormous distances across three continents; if it was not for the compassionate & righteous principals Muslims carried with them.
Although Muslims were not forcing their subjects to convert to Islam, the majority selected to convert and many became devoted and loyal Muslims, and many proved to be prominent Moslem scholars and philosophers. None of the great conquerors such as Alexander the Great or the Mongol left such effect on the lands they conquered; on the contrary, they dissolved and disappeared in such societies and religions.
Islam have granted all people the right to freely choose their religion and beliefs, there was no conversion by force:
{There is no compulsion in religion, the Right Path has indeed been made distinct from the wrong; so whoever rejects the Taghut [devil الطاغوت], and believes in Allah, he has then grasped the firm handle, no breaking for it ….} Al-Quran 2:256.
In addition, Christians and Jews were considered to be the People of the Book, which was revealed to their profits by Allah. The following Quran verses describe the views Muslims have with regard to the Jewish and the Christians:
{Say: We believe in Allah and in what has been revealed to us and what was revealed to Abraham, Isma’il, Isaac, Jacob, and the Tribes, and in what was given to Moses, Jesus, and the Prophets, from their Lord: We make no distinction between them ….} Al Quran 3:84.
Historically, tolerance for the ‘people of the book’ (Jews and Christians) has been a feature of Muslims belief and practice. Christian and Jews lived peacefully side by side with Moslems in all the lands governed by Islam throughout the history.
Arabia before Islam
Arabian Peninsula before Islam had been a culturally isolated and economically underdeveloped region. Most of the land is arid and desert; rainfall is scarce, vegetation scant, and very little of the land is suitable for agriculture. In the north of the region, several Arabian kingdoms were able to establish contacts with the Byzantine and the Persian Sassanian empires as early as the fifth century A.D. To the south, small Arabian kingdoms, including Saba (Sheba), were ancient centers of Arabic civilization. But in the interior, dotted only with occasional oases, the nomadic life was the only successful existence.
Early Makkah
On the western side of the Arabian Peninsula is a region known as Hejaz, or “barrier.” The Hejaz rises from the western coastal plain from Yemen in the south to the Sinai Peninsula in the north. One of the towns in the Hejaz is Makkah, set among the barren hills fifty miles inland from the sea. Makkah had several advantages: two ancient trading caravan routes met there, possessed a well (Zamzam) of great depth, and another significant advantage of Makkah was its importance as a religious sanctuary. An ancient temple stood in the center of Makkah. Known as the Kaaba (cube), this House of worship was built by Abraham and his son Ismail, above an older existing foundation,
{And when Ibrahim and Ismael were raising the foundations of the House, (they prayed): Our Lord Accept this work from us. You are the All-hearing, All-knowing} Al-Quran 2:127.
{Indeed, the first House [of worship] established for mankind was that at Makkah blessed and a guidance for the worlds} Al Quran 3:96
For centuries the Kaaba had been a holy place of annual pilgrimage for the Arab tribes and a focal point of Arabic cultural and linguistic unity. It started at the time of Ismail as the House of worship for the one God, but after century’s people lost their way and deviated to paganism worshiping many false gods, by the time of the birth of Islam, the Kaaba was accommodating the shrines of many Idols (Asnam الأصنام).
The Birth of Islam:
Muhammad ibn Abdullah (saas) a was born in Makkah in the year 570 AC. He earned his living as a trader and was known by his people as al-amin (the trustworthy one). When Muhammad (saas) reached the age of 40, the angel Gabriel came to him with revelations that established his prophet hood. Muhammad (saas) was first ordered to instruct his immediate family on Islam, and soon after it was revealed to him to begin delivering the message to all mankind. In the next 23 Hijri years, he communicated the message of Allah to all people in the Arabian Peninsula, and set an example for how each man and woman should lead his and her life.
Early Islam appealed particularly to the poor and oppressed in the society. Muhammad made no social, racial or economic distinctions among his followers: all Muslims were (and are) equal in the sight of God. Thus Islam also offered the Arab tribes a way out of the interminable blood feuds which characterized pre-Islamic Arabia. As he gained support in his hometown of Makkah, Muhammad became a threat to the established political and religious order there, because Makkah, with its sacred Kaaba, was the center of the traditional pagan Arab religious and economic system. As they fought the new religion and tried to kill him, He and his followers fled Makkah in 622 for Madina, a town troubled by tribal feuds, to which he was invited as Allah’s Messenger. His flight to Madina marked the start of the Muslim Hijri calendar.
The Prophet Muhammed (saas) and his Makkan followers were received in Madinah with greetings and brotherly love. On his arrival, he immediately put in place the covenants and rules to govern the relations between the new comers and the different factions of its inhabitants, also protecting the rights of the Madinah’s Jews, and successfully resolving the Madinah’s internal disputes, thus gaining great authority and credibility. Three years later, war erupted with the Makkan army, in a famous battle (at a place named Badr) fought in 624 (3 AH) the Muslims, though greatly outnumbered, defeated their opponents and gained further credibility for their religion. Six years later (630, 9 AH) they took Makkah itself and, purifying the Kaaba of pagan associations, made it a central point of the new religion. Before the death of the Prophet (saas) in 632 (11 AH) All the inhabitants of the Arabian Peninsula have joined Islam.
The Historical Progress of the Islamic Nation:
The great power of the Islamic teachings enabled the fragmented Arab tribes to unify and expand across three continents in an astoundingly brief period.
During the reigns of the first four caliphs and the century of during the Umayyad Dynasty (661-750), great strides were made in expanding and gaining new territories and peoples.
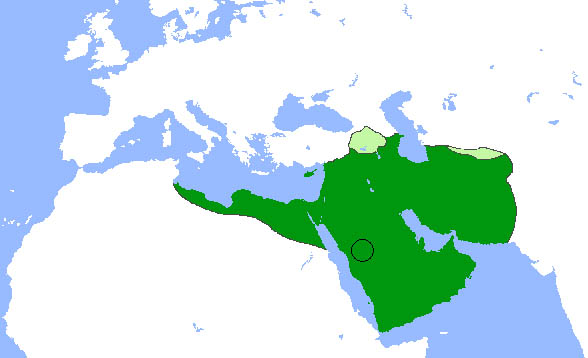
Expansion During The Period Of The Four Caliphs (Al Khulfaa’ Al Rashidun) (632-661) Only 29 Years
The Umayyad Khilafa (Dynasty)
Though Makkah remained the holy city of Islam, under the Umayyads the political center of community shifted to Damascus in Syria, where the Umayyads chose to reside after the murder of Uthman. From Damascus a succession of Umayyad caliphs strove to build a bureaucracy that would bind together the vast domains they claimed to rule.
After a pause to settle internal disputes over succession, the remarkable sequence of Arab conquest was renewed in the last half of the 7th century. Muslim armies broke into central Asia, thus inaugurating a rivalry with Buddhism in the region that continues to the present day. By the early 8th century, the eastern point of this advance had reached into northwest India.
Far to the west, Arab armies swept across North Africa and crossed the Straits of Gibraltar to conquer Spain and threaten France. Though the Muslim advance into Western Europe was in effect checked by the hard-fought victory of Charles Martel and the Franks at Poitiers in 732, the Arabs did not fully retreat beyond the Pyrenees into Spain until decades later. Muslim warriors and sailors dominated much of the Mediterranean, a position that would be solidified by the conquest of key islands, such as Crete, Sicily, and Sardinia, in the early decades of the 9th century. By the early 700s, the Umayyads ruled an empire that extended from Spain in the west to the steppes of central Asia in the east. Not since the Romans had there been an empire to match it; never had an empire of its size been built so rapidly.
The Umayyad Islam Nation (years 661 – 750)
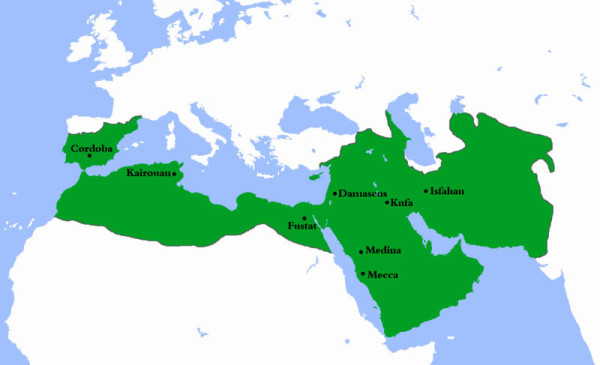
The Abbasid Khilafa (Dynasty)
In 750 the Umayyad Dynasty was removed from power, and a new dynasty, the Abbasid, ruled most of the Muslim world from year 750 to 1258. The city of Baghdad was built in 762 as the capital of the new caliph, Abu-al-Abbas, a descendant of the Prophet’s uncle.
The Abbasid Dynasty marked the high point of Islamic power and civilization. The empire ruled by these caliphs was greater in size than the domain of the Roman Caesars; it was the product of an expansion during which the Muslims assimilated peoples, customs, cultures, and inventions on an unprecedented scale. This Islamic state, in fact, drew from the resources of the entire known world
During the early Abbasid period Islam reached the high point of its geographical expansion and cultural achievements, extending from Spain across three continents to East Asia. Unparalleled prosperity evolved from a combination of successful trade, industry, and agriculture.
The Muslims were especially gifted in science, literature, and philosophy. Muslim intellectual life was in large part the product of a genius for synthesizing varying cultures, and the diffusion of this knowledge was a tremendous factor in the revival of classical learning and the coming of the Renaissance in Europe.
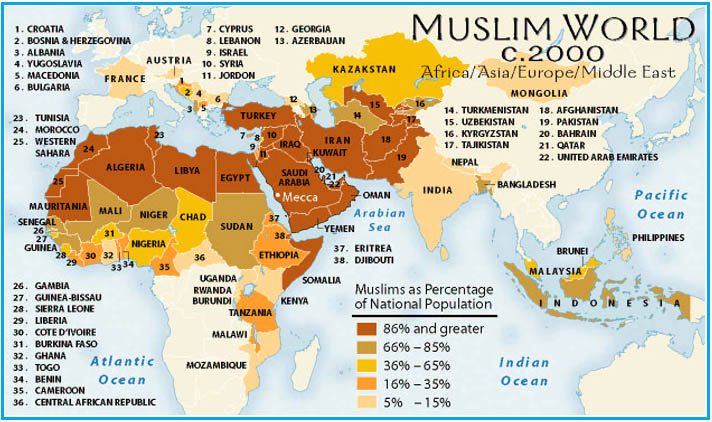
Islam Today
With almost one of every 4 living on the planet is Muslim, Islam is a major force in the world today.
The Nation of Islam, founded by the descendants of Ismail, is indeed the Great Nation, promised by Allah as told in Genesis chapter 21, 18 when the Angels spoke on the name of God to Hagger:
“Arise, lift up the lad, and hold him in thine hand; for I will make him a great nation.”
.
.
- صلى الله عليه وسلم Peace Be Upon Him (back)